Support / Contact Us
ILCE-1
Use the size of the subject on screen as a rough guide to decide the size of the focus area, such as [Spot] .

For [Spot], the subject should be large enough to cover the whole focus area. Having the subject at this size avoids the focus drifting to the background.
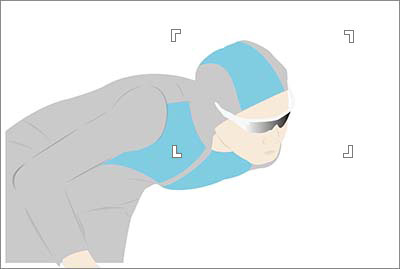
For [Expand Spot], the focus area including the expanded area should just about overlap with the subject.
The optimal Focus Area size for the same skating scene depends on the subject size on screen.
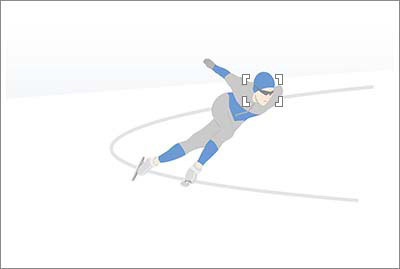
[Spot: M] is recommended for focusing on the subject’s face. If set to [Zone], other features such as line markings on the skate rink will be inside the area and the camera might focus on these instead of on the skater.
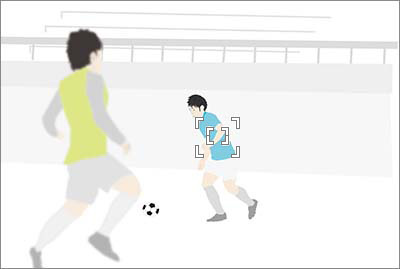
To target a fast-moving subject at this size using a long focal length, try a wider setting such as [Zone]. If the situation requires switching between holding the camera horizontally and vertically, set [Switch V/H AF Area] to [AF Point Only].
American football and ice hockey may look like they need similar settings, but there are subtle differences in how to better shoot them.

In American football and rugby, where players come together and clash, [Expand Spot] will pinpoint the subject more accurately.

For sports like ice hockey where the subject is moving fast, try keeping the Focus Area to the same size as a player (M in the example above). If the area is too large and includes several players, the camera may not focus on the right one.
If a subject is moving slowly or predictably, a small-area setting like [Expand Spot] will focus accurately on the target position. If a subject is moving at high speed or unpredictably, a wider focus area setting such as [Wide] maintains focus while allowing the composition to be adjusted.
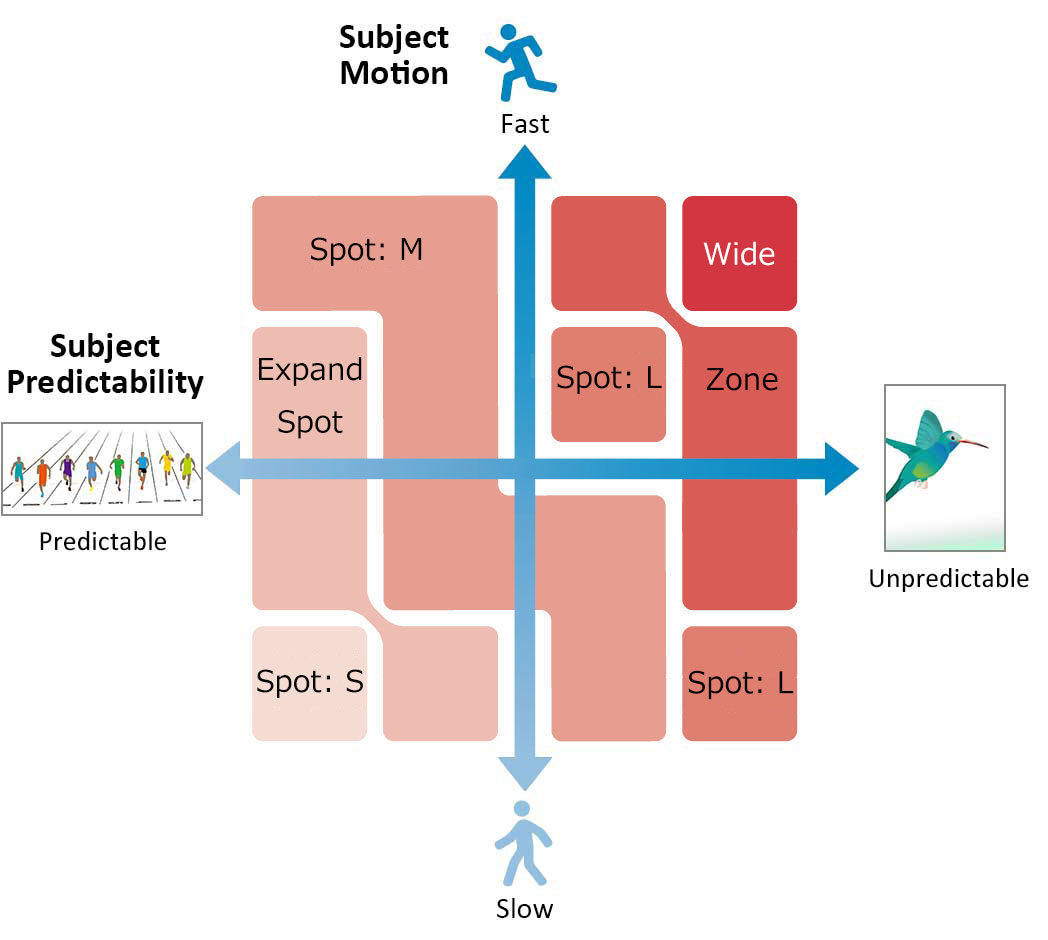
AF-C Focus Mode has five levels of focus tracking.
[1(Locked on)] to [2]: Low tracking sensitivity (prioritizes stability)
Focus position is stable and stays locked on to the selected subject.
[4] to [5(Responsive)]: High tracking sensitivity (prioritizes responsiveness)
The camera focuses quickly on nearby subjects instead of tracking a single subject.
As a rough guide, this setting should be [2] when tracking a specific player in a sport like American football where players are close together, or [3(Standard)] if someone is passing in front of the subject.
In soccer, the players are generally farther apart so [4] is the most suitable setting as it prioritizes responsiveness over lock-on. When set to [4], the focus will not shift if another player’s arm passes in front of the subject, but the focus will move to another player if their whole body blocks the original subject.
Try [Balanced Emphasis], which provides a good balance between the existing [AF] and [Release] settings. This function is useful for maintaining accurate focus while catching a crucial moment when shooting a moving object.
[AF]
The shutter cannot be released before the subject is in focus. Use this setting to prioritize focus over the speed of continuous shooting.
(The continuous shooting speed may become slower and/or the shooting interval may become uneven, depending on the scene.)
[Release]
This setting allows you to shoot at any time, but at the risk of shooting multiple images that are out of focus. It is useful for maintaining the speed of continuous shooting.
[Balanced Emphasis]
The subject is more likely to be in focus than when using [Release]. The continuous shooting speed will be slightly slower than when using [Release]. As the camera determines the shooting method immediately before the release timing, this setting is recommended for shooting moving objects. Use [Release] when timing has greater priority.
Comparison between [Balanced Emphasis] and [Release]
The advantage of [Release] is that it maintains the continuous shooting interval even if the subject moves a lot. It is useful for shooting a series of continuous pictures or making a movie.
Take photographing a player kicking the ball in soccer as an example. [AF] may miss the moment of the kick, while [Release] will capture the moment but all the shots may be out of focus. [Balanced Emphasis] will give some usable shots.
Choose whether to adjust the position of the focusing frame (AF point) and Focus Area settings to the camera orientation (horizontal/vertical). The default setting is [Off], but [AF Point Only] is recommended if changing the camera orientation frequently, such as reorienting the camera vertically when the subject comes closer.
[Off]

[AF Point Only]

[AF Point + AF Area]

 Silent Mode Settings]
Silent Mode Settings]When you shoot an image in a scene that requires silence, it is difficult to shoot with a mechanical shutter because it produces shutter sounds. In such a situation, the silent mode is very useful since it enables shooting without shutter sounds or electronic sounds. When [Silent Mode] is set to [On], [Shutter Type] and [Shutter Type in Interval] become locked to [Electronic Shutter], and [Audio signals] becomes locked to [Off].
Furthermore, for [Target Function Settings], you can also set whether or not to simultaneously change the settings for other functions that emit sounds from the camera when the camera is set to the silent mode.
