Focusing on the eyes of an animal or bird (Shooting movies)
The following procedure is used to focus on the eyes of an animal or bird.
There are three shooting methods. Use the method that is suitable according to the shooting conditions.
- We recommend this when you want to easily focus on a subject by touching it on the monitor to select it.
- When you want to focus on a subject with higher priority on the eye but want to continue focusing using [
 Focus Area] in case detecting an eye is difficult.
Focus Area] in case detecting an eye is difficult.
- When you want to focus temporarily on an eye within the whole range of the monitor, regardless of the setting for [
 Focus Area]
Focus Area]  To temporarily focus on an eye using [Subject Recognition AF] after focusing on the subject using (Manual Focus)
To temporarily focus on an eye using [Subject Recognition AF] after focusing on the subject using (Manual Focus)
When you want to focus on an eye by touch operation ([Touch Tracking])
Setting the camera
-
Still/Movie/S&Q switch
Select
 movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
-
[
 Subject Recog in AF]
Subject Recog in AF]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Subject Recog in AF] → [On]
Subject Recog in AF] → [On] -
[
 Recognition Target]
Recognition Target]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird].
Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird]. -
[
 Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On] -
[Touch Operation]
MENU →
 (Setup) → [Touch Operation] → [Touch Operation] → [On].
(Setup) → [Touch Operation] → [Touch Operation] → [On]. -
[Shooting Screen]
MENU →
 (Setup) → [Touch Operation] → [Shooting Screen] → select menu item and then perform the following settings.
(Setup) → [Touch Operation] → [Shooting Screen] → select menu item and then perform the following settings.- [Shooting Screen]: [On]
- [Touch Func. in Shooting]: Select [Touch Tracking] or [TouchTracking+AE].
Hint
If you register [Touch Func. in Shooting] on the function menu, you can also change the settings of [Touch Func. in Shooting] by touching this icon.
Related camera help guide
Guide to using the camera
Focusing on an eye by touch operation ([Touch Tracking])
Select an area close to the eye of a subject by touch operation ([Touch Tracking]).
When the eye of the subject is recognized, a white frame appears around the eye and focusing can be continued.
Condition where a subject-recognition frame (white) appears around the eye
Hint
If you set [Touch Func. in Shooting] to [TouchTracking+AE], the brightness will be set according to the subject you touched. This will also allow you to fine-tune the brightness by sliding the brightness adjustment bar that appears after touching.
Note
- The camera may not recognize an eye depending on a subject or shooting conditions.For details, refer to “About an easy-to-recognize subject.”
- It is easier to focus on an eye if you touch the eye by setting touch tracking when the eye is out of focus.
- Select a lower value for [AF Subj. Shift Sensitivity] when subject recognition is frequently interrupted so that the focus remains steady.
- When photographing small, fast-moving subjects such as insects, using a faster shutter setting can contribute to better recognition.
Operating the tracking and subject recognition functions together and priorities and limit of the part to be recognized
When [ Subject Recog in AF] is set to [On], the focus frame will automatically move to a recognized part of a subject if the part, such as an eye, is detected while the subject is being tracked using the tracking function.
Subject Recog in AF] is set to [On], the focus frame will automatically move to a recognized part of a subject if the part, such as an eye, is detected while the subject is being tracked using the tracking function.
The camera automatically selects the part (in the order of eye, head, and body) to focus on with priority. If the camera cannot focus on the body, it starts tracking.
The following procedure is used under the condition where [ Recognition Target] is set to [Animal].
Recognition Target] is set to [Animal].
-
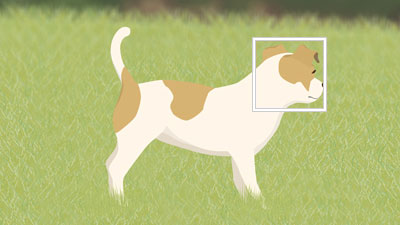
Tracking distant subjects

-
The body of a subject is recognized when the subject being tracked is getting closer.

-
An eye of a subject is recognized when the subject being tracked is getting even more closer.

-
If the camera cannot recognize an eye because the subject is turned away, the camera will recognize the head or body.
Note
- The subject-recognition frame sometimes appears on a subject or part of a subject that is different from those set by [
 Recognition Target]. Some types of animals or some parts of birds cannot be recognized in line with the [
Recognition Target]. Some types of animals or some parts of birds cannot be recognized in line with the [ Recognition Target] setting.
Recognition Target] setting.
Switching the eye to detect
* When the subject is a bird, you cannot switch between left and right eyes, on which the camera focuses.
When you touch around an eye on the monitor, you can switch the eye on which the camera will focus.
Touch around an eye on which you would like to focus on the monitor
The eye on which the camera will focus will be switched
When you want to focus on an eye using the focus area
Setting the camera
-
Still/Movie/S&Q switch
Select
 movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
-
[
 Subject Recog in AF]
Subject Recog in AF]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Subject Recog in AF] → [On]
Subject Recog in AF] → [On] -
[
 Recognition Target]
Recognition Target]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird].
Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird]. -
[
 Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On] -
[
 Focus Mode]
Focus Mode]MENU →
 (Focus) → [AF/MF] → [
(Focus) → [AF/MF] → [ Focus Mode] →
Focus Mode] →  [Continuous AF].
[Continuous AF]. -
[
 Focus Area]
Focus Area]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Focus Area] → [
(Focus) → [Focus Area] → [ Focus Area] → the desired setting.
Focus Area] → the desired setting.
Guide to using the camera
Focus on an eye using [ Focus Area]
Focus Area]
Since the camera focuses on an eye of an animal or bird in the focus area, if you want to detect a part of the subject such as the eye using the widest possible range, set [ Focus Area] to [Wide] in advance.
Focus Area] to [Wide] in advance.
If you want to limit the range for detecting an eye, set [ Focus Area] to settings such as [Spot] or [Zone].
Focus Area] to settings such as [Spot] or [Zone].
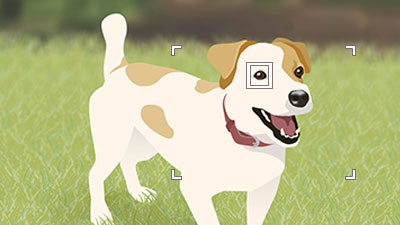
Example of condition where the camera can focus on an eye
The following procedure is used under the condition where [ Recognition Target] is set to [Animal].
Recognition Target] is set to [Animal].
-
Point the camera so that the animal’s eye to be focused on are within the focus area.

When [
 Focus Area] is set to [Zone]
Focus Area] is set to [Zone] -
When the camera is able to focus on the eye of the animal, a white subject-recognition frame appears around the eye.
Hint
- When you want to switch [
 Recognition Target] quickly, you may find it convenient if you set [Recog. Target Select] to a custom key.
Recognition Target] quickly, you may find it convenient if you set [Recog. Target Select] to a custom key. - To make it easier to focus on a specific subject's eye when the face of an animal displayed on the screen is small or when multiple animals are displayed, select the subject to be tracked by activating touch operation or set [
 Focus Area] to [Spot] and then focus on the subject.
Focus Area] to [Spot] and then focus on the subject.
Note
- The camera may not recognize an eye depending on a subject or shooting conditions.For details, refer to “About an easy-to-recognize subject.”
- When bodies of animals in the focus area are overlapping, the camera will perform focusing with priority in the order of eye, head, and body even if no eyes are detected in the focus area.

- When you want to switch [
Switching the eye to detect
* When the subject is a bird, you cannot switch between left and right eyes, on which the camera focuses.
You can set whether to focus on the left or right eye in advance by selecting MENU →  (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Right/Left Eye Select]. You can also switch the eye using the following procedure.
Right/Left Eye Select]. You can also switch the eye using the following procedure.
Switching with a custom key assigned to [Switch Right/Left Eye]
* [Switch Right/Left Eye] operations are possible when you are not pressing the shutter button halfway down.
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Right Eye] or [Left Eye], each time you press the custom key to which [Switch Right/Left Eye] is assigned, you can switch the eye on which the camera will focus.
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Right Eye] or [Left Eye], each time you press the custom key to which [Switch Right/Left Eye] is assigned, you can switch the eye on which the camera will focus.
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], you can temporarily switch the eye to be focused by pressing the custom key to which you have assigned the [Switch Right/Left Eye].
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], you can temporarily switch the eye to be focused by pressing the custom key to which you have assigned the [Switch Right/Left Eye].
Note
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], the temporary left/right selection is canceled when you perform the following operations, and the camera returns to automatic eye selection.
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], the temporary left/right selection is canceled when you perform the following operations, and the camera returns to automatic eye selection.
- Pressing the center of the control wheel
- Pressing the MENU button
Tracking from the focus area position
- You can use [Tracking On] or [Tracking on Toggle] to start tracking by operating a custom key.
- When the focus area is set to [Center Fix], [Spot], or [Expand Spot] in advance, tracking starts from the position of the set focus area.
- When the focus area is set to [Wide] or [Zone] in advance, tracking will start from the position of the subject recognized in the area.
- Tracking is performed in the entire screen (during tracking) regardless of the focus area setting.
- Focusing on a subject by pressing a custom key to which [Tracking On] is assigned
While the assigned custom key is pressed, the camera continues to track a subject. - Focusing on a subject by pressing a custom key to which [Tracking on Toggle] is assigned
When you press the custom key, the camera starts tracking the subject. When you press the custom key again, the camera stops tracking.
- Focusing on a subject by pressing a custom key to which [Tracking On] is assigned
- To use a custom key, perform the following setting in advance.
Select MENU → (Setup) → [Operation Customize] → [
(Setup) → [Operation Customize] → [ Custom Key/Dial Set.], select a button to which the function is assigned, and then set
Custom Key/Dial Set.], select a button to which the function is assigned, and then set  (Focus) → [Focus Area] → [Tracking On] or [Tracking on Toggle].
(Focus) → [Focus Area] → [Tracking On] or [Tracking on Toggle]. - You can use tracking by operating the custom key even when the focus mode is set to manual focus.
Focusing on an eye using a custom key to which the [Subject Recognition AF] function is assigned
Setting the camera
-
Still/Movie/S&Q switch
Select
 movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
movie shooting mode using the Still/Movie/S&Q switch.
-
[Custom Key/Dial Set.]
Select MENU →
 (Setup) → [Operation Customize] → [
(Setup) → [Operation Customize] → [ Custom Key/Dial Set.], select a button to which the function is assigned, and then set
Custom Key/Dial Set.], select a button to which the function is assigned, and then set  (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [Subject Recognition AF].
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [Subject Recognition AF].* You may not be able to select [Subject Recognition AF] depending on the assigned buttons.
-
[
 Recognition Target]
Recognition Target]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird].
Recognition Target] → [Animal], [Bird] or [Animal/Bird]. -
[
 Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.]MENU →
 (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On]
Sbj Recog Frm Disp.] → [On]
Guide to using the camera
Focusing on an eye by pressing a custom key to which [Subject Recognition AF] is assigned
When you press a custom key to which [Subject Recognition AF] is assigned and the camera recognizes the eye of an animal or bird, a white subject-recognition frame appears. If you zoom in on a subject under the condition where the eye cannot be recognized, the subject-recognition frame may appear around the eye in some cases.
Note
- The camera may not recognize an eye depending on a subject or shooting conditions.For details, refer to “About an easy-to-recognize subject.”
Switching the eye to detect
* When the subject is a bird, you cannot switch between left and right eyes, on which the camera focuses.
You can set whether to focus on the left or right eye in advance by selecting MENU →  (Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [
(Focus) → [Subject Recognition] → [ Right/Left Eye Select]. You can also switch the eye using the following procedure.
Right/Left Eye Select]. You can also switch the eye using the following procedure.
Switching with a custom key assigned to [Switch Right/Left Eye]
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Right Eye] or [Left Eye], each time you press the custom key to which [Switch Right/Left Eye] is assigned, you can switch the eye on which the camera will focus.
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Right Eye] or [Left Eye], each time you press the custom key to which [Switch Right/Left Eye] is assigned, you can switch the eye on which the camera will focus.
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], you can temporarily switch the eye to be focused by pressing the custom key to which you have assigned the [Switch Right/Left Eye].
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], you can temporarily switch the eye to be focused by pressing the custom key to which you have assigned the [Switch Right/Left Eye].
Note
When [ Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], the temporary left/right selection is canceled when you perform the following operations, and the camera returns to automatic eye selection.
Right/Left Eye Select] is set to [Auto], the temporary left/right selection is canceled when you perform the following operations, and the camera returns to automatic eye selection.
- Pressing the center of the control wheel
- Pressing the MENU button
About an easy-to-recognize subject
In some cases, the camera may not be able to recognize an eye, head, or body depending on the type of animal or bird, orientation of a face, size of a subject, and shooting conditions such as a scene where multiple subjects are moving around.
Use the following examples as guidelines.
- Example of easy-to-recognize [Animal]
- Example of hard-to-recognize [Animal]
- Example of easy-to-recognize [Bird]
- Example of hard-to-recognize [Bird]
Example of easy-to-recognize [Animal]
Example of subjects with easy-to-recognize eyes

Cat-like face

Dog-like face

Some herbivorous animals

Some herbivorous animals
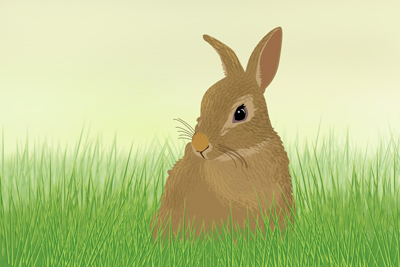
Some small animals

Some small animals

Size and direction of a subject where its entire face such as an eye or nose is seen properly
(Example:Face shown in front view)

Size and direction of a subject where its entire face such as an eye or nose is seen properly
(Example: Face shown sideways)
Example of a subject with an easy-to-recognize head or body

Cat-like form

Dog-like form
Example of hard-to-recognize [Animal]
Example of a subject with a hard-to-recognize eye

Animals that have faces significantly different from those of “Cats” and “Dogs”

Animals that have faces significantly different from those of “Cats” and “Dogs”

Face or body with markings

The face of the subject is facing down or backward, or part of the face is hidden.
Example of a subject that has a hard-to-recognize head or body

Animals that have forms significantly different from those of “Cats” and “Dogs”
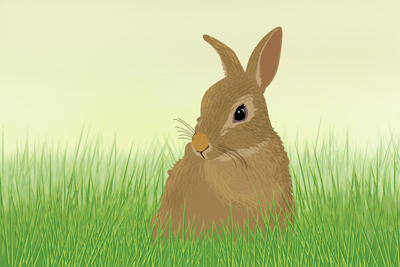
Animals that have forms significantly different from those of “Cats” and “Dogs”

Animals that have forms significantly different from those of “Cats” and “Dogs”

Animals with complicated postures

A part of the body is hidden.
Example of subject with generally hard to recognize eyes, head, or body

Multiple animals in a confined area

Moving around

Backlit or dark locations

Animals with black hair or not distinguishable face
Hint
- The camera may find it difficult to recognize a subject when the head of an animal is not in focus. In that case, focus on the head once. After that, the camera will recognize the subject more easily.
Example of easy-to-recognize [Bird]
Example of subjects with easy-to-recognize eyes

Face like that of small birds

“Raptor-like” face

“Water fowl-like” face

Entire face of the subject is seen properly and it is not too small

Direction of face where the shape of an eye and beak is seen properly

Direction of face where the shape of an eye and beak is seen properly
Example of a subject with an easy-to-recognize head or body

“Small bird-like” form

“Raptor-like” form

“Water fowl-like” form

Not-too-small size where the head or entire body is properly visible

Not-too-small size where the head or entire body is properly visible
Example of hard-to-recognize [Bird]
Example of a subject with a hard-to-recognize eye

Birds that have faces different from “small birds”, “eagles/hawks”, and “water fowls ”
(Example: Birds with complicated crests and tufted heads)

Cases where an eye or body outline of bird is not sharp
(Example: Patterns of body feathers make it difficult to identify eyes)

Cases where an eye or body outline of bird is not sharp
(Example: Dark environment, black body feathers)

Cases where an eye or body outline of bird is not sharp
(Example: Colors or patterns of body feathers that are similar to the background)

Scene where many birds have flocked together
Example of a subject that has a hard-to-recognize head or body

Birds that have complicated forms due to a crest, etc.
(Example: Birds with complicated crests and tufted heads)

Case where the contour of a bird is not distinguishable
(Example: Complicated posture)

Case where the contour of a bird is not distinguishable
(Example: A part of the body is hidden)

Case where the contour of a bird is not distinguishable
(Example: Dark locations)

Case where the contour of a bird is not distinguishable
(Example: Colors or patterns of body feathers that are similar to the background)

Scene where many birds have flocked together
Hint
- When the head of a bird is not in focus, the camera may not be able to recognize the subject easily. In that case, focus on the head once. After that, the camera will recognize the subject more easily.
*The menu screen images on this web page have been simplified for display purposes, and do not exactly reflect the actual screen display of the camera.